Objective: The objective is to investigate the association between gross motor function, functional independence, and quality of life (QoL) in children with cerebral palsy (CP) in the West Bank, Palestine.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using the CP-QoL measure, Functional Independence Measure (FIM), and Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS). A 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Least Significant Difference post-hoc analysis was used to compare total FIM scores across GMFCS levels. Correlations between GMFCS, FIM, and CP-QoL domains were examined using Pearson’s or Spearman’s coefficients based on data distribution. Statistical significance was set at P < .05.
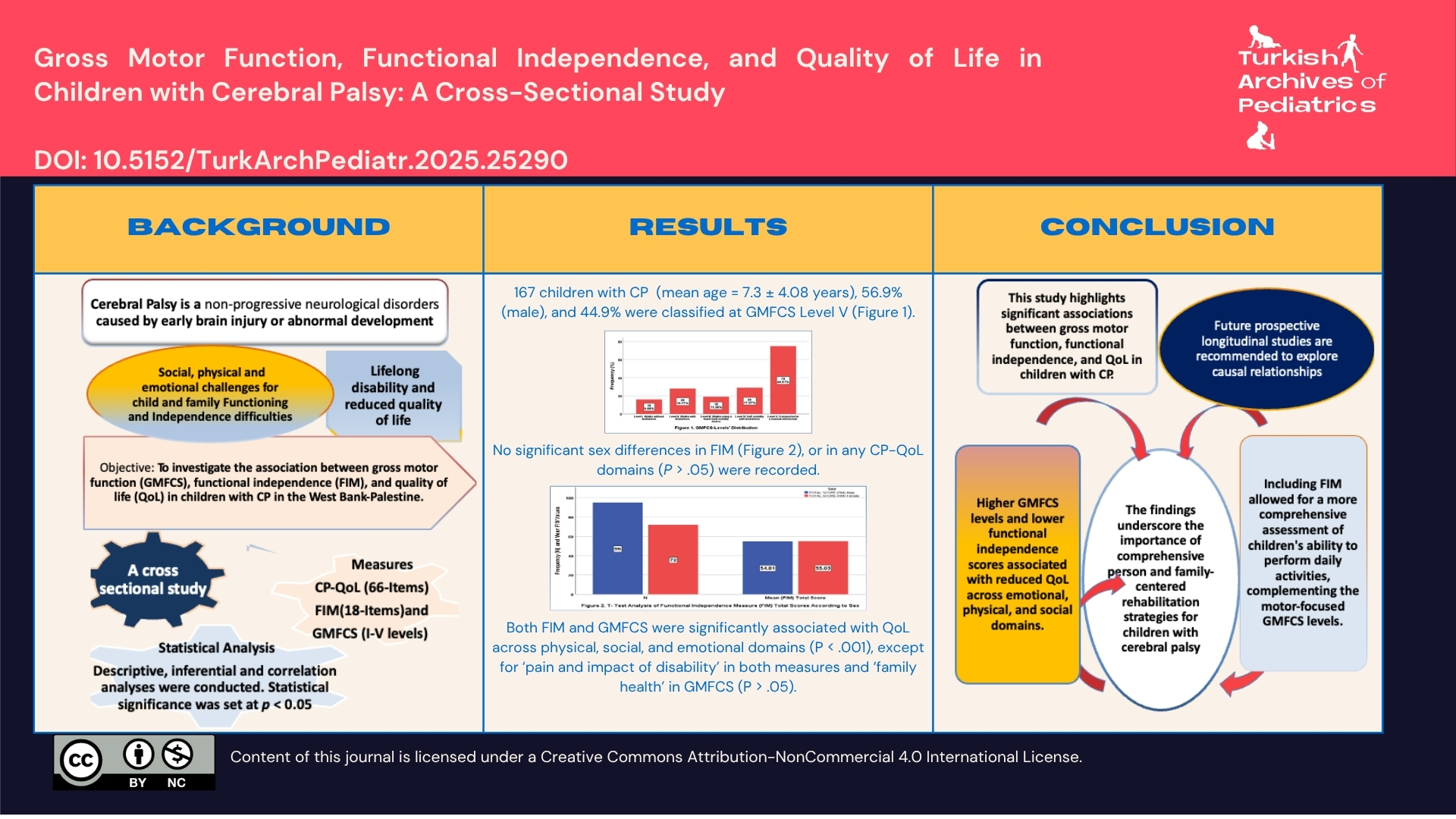
Results: The study included 167 children with CP (mean age 7.3 ± 4.08; range 3-18 years; 56.9% male). Spastic quadriplegia (35.3%) and GMFCS Level V (44.9%) were the most common. A strong negative correlation was found between GMFCS level and total FIM score (r = −0.696, P < .001). The correlation results showed that both FIM and GMFCS were significantly associated with QoL across multiple domains, including physical, social, and emotional well-being (P < .001), except for the “pain and impact of disability” domain in both measures and the “family health” domain in GMFCS (P > .05).
Conclusion: This study highlights significant associations between gross motor function, functional independence, and QoL in children with CP. Higher GMFCS levels and lower FIM scores are associated with reduced QoL across emotional, physical, and social domains. Although the cross-sectional design limits causal inference, the findings underscore the importance of comprehensive, person- and family-centered rehabilitation strategies for children with CP.
Cite this article as: Halaweh H, Abumaizer R, Kharraz A, Hroub R, Ahmad Z. Gross motor function, functional independence, and quality of life in children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional study. Turk Arch Pediatr. Published online October 20, 2025. doi:10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2025.25290.



.png)